DPP6: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
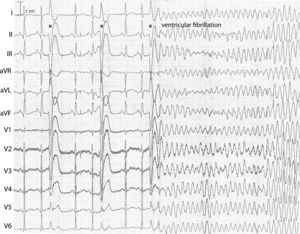
[[File:DPP6ECG.jpg|thumb|ECG recording of idiopathic ventricular fibrillation (IVF) in a risk haplotype carrier. The short coupled ventricular extrasystoles from the right ventricular apex/lower free wall (indicated by asterisks) first result in compensatory pauses and then in IVF requiring external defibrillation]] | [[File:DPP6ECG.jpg|thumb|ECG recording of idiopathic ventricular fibrillation (IVF) in a risk haplotype carrier. The short coupled ventricular extrasystoles from the right ventricular apex/lower free wall (indicated by asterisks) first result in compensatory pauses and then in IVF requiring external defibrillation]] | ||
A new arrhythmia gene on chromosome 7q36, DPP6, is linked to familial IVF and shows a very malignant phenotype. This phenotype consists of cardiac arrest by IVF at young age, which is elicited by short coupled extrasystoles | A new arrhythmia gene on chromosome 7q36, DPP6, is linked to familial IVF and shows a very malignant phenotype. This phenotype consists of cardiac arrest by IVF at young age, which is elicited by short coupled extrasystoles. Affected patients can be offered preventive treatment accordingly. When closely coupled extrasystoles initiate ventricular fibrillation in the absence of other identifiable causes, a link to the DPP6 gene should also be suspected.<cite>Postema</cite> | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<biblio> | <biblio> | ||
#Postema pmid=21512816 | #Postema pmid=21512816 | ||
</biblio> | </biblio> | ||
Revision as of 19:38, 17 January 2012
A new arrhythmia gene on chromosome 7q36, DPP6, is linked to familial IVF and shows a very malignant phenotype. This phenotype consists of cardiac arrest by IVF at young age, which is elicited by short coupled extrasystoles. Affected patients can be offered preventive treatment accordingly. When closely coupled extrasystoles initiate ventricular fibrillation in the absence of other identifiable causes, a link to the DPP6 gene should also be suspected.[1]