ARVC/D: Difference between revisions
(Created page with "thumb|ECG with an epsilon wave in V1 [[Image:arvdhart.png|thumb| A section throughout the heart of an ARVC patient. (A) Transmural fatty replacement of...") |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
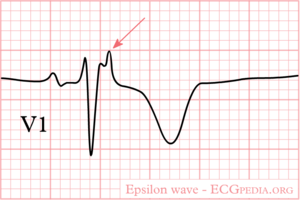
[[Image:epsilon_wave.png|thumb|ECG with an epsilon wave in V1]] | [[Image:epsilon_wave.png|thumb|ECG with an epsilon wave in V1]] | ||
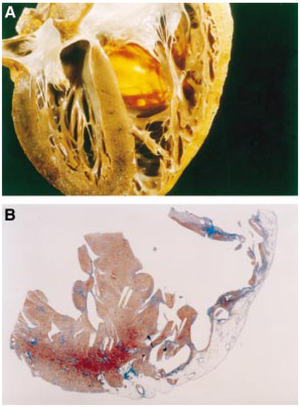
[[Image:arvdhart.png|thumb| A section throughout the heart of an ARVC patient. (A) Transmural fatty replacement of the right ventricular free wall. (B) Myocardial atrophy is confined to the right ventricle and substantially spares the interventricular septum as well as the left ventricular free wall. <cite>Corrado</cite> Reproduced with permission from BMJ Publishing Group Ltd. ]] | [[Image:arvdhart.png|thumb| A section throughout the heart of an ARVC patient. (A) Transmural fatty replacement of the right ventricular free wall. (B) Myocardial atrophy is confined to the right ventricle and substantially spares the interventricular septum as well as the left ventricular free wall. <cite>Corrado</cite> Reproduced with permission from BMJ Publishing Group Ltd. ]] | ||
'''Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy''', (ARVC, or ARVD: Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Disease) is characterized by fatty replacement and fibrosis of the heart. Most commonly the right ventricle apex and outflow tract are involved. However the left ventricle can be affected to.<cite>Corr</cite> | '''Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy''', (ARVC, or ARVD: Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Disease, the latest name is AC Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathy) is characterized by fatty replacement and fibrosis of the heart. Most commonly the right ventricle apex and outflow tract are involved. However the left ventricle can be affected to.<cite>Corr</cite> | ||
As a result of the fatty replacement and fibrosis, ventricular arrhythmias are common in this disease and can lead to palpitations, syncope and sudden death. At more advanced ages right ventricular pump failure can occur. | As a result of the fatty replacement and fibrosis, ventricular arrhythmias are common in this disease and can lead to palpitations, syncope and sudden death. At more advanced ages right ventricular pump failure can occur. | ||
Revision as of 17:31, 31 October 2012
Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy, (ARVC, or ARVD: Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Disease, the latest name is AC Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathy) is characterized by fatty replacement and fibrosis of the heart. Most commonly the right ventricle apex and outflow tract are involved. However the left ventricle can be affected to.[2]
As a result of the fatty replacement and fibrosis, ventricular arrhythmias are common in this disease and can lead to palpitations, syncope and sudden death. At more advanced ages right ventricular pump failure can occur.
The diagnosis is based on major and minor criteria, as published by the European Society of Cardiology.[3]
ARVC is a progressive disease. The incidence is estimated to be 1:3.000-1:10.000. Manifestations are usually seen in teenagers. Although the diagnosis is more often made in athletes, sports are not thought to have a causative relationship with the disease. ARVD can occur in families; more than 9 different chromosomal defects have been described, most often with autosomal dominant inheritance.
One unique form of ARVD, called Naxos disease (after the Greek island where it was first diagnosed), has an autosomal recessive pattern of inheritance.
Diagnosis ARVC is a difficult diagnosis to make. Therefore, the European Society of Cardiology has created a list of diagnostic criteria for the diagnosis of ARVC[3] (see table). An [arvc.ca/pdg/public.php?rep=arvc_cri online calculator] can help in assessing the risk in an individual patient. In 2009 these criteria were updated[4][5], see the table below.
Treatment focuses on avoiding complications.[6]
- Medication:
- Anti-arrhythmics: Sotalol better than Amiodarone.
- ACE-inhibitors to prevent cardiac remodelling
- ICD implantation is recommended for the prevention of sudden cardiac death in patients with ARVC with documented sustained VT or VF who are receiving chronic optimal medical therapy.
- ICD implantation can be considered for the prevention of sudden cardiac death in patients with ARVC with extensive disease, including those with left ventricular involvement, 1 or more affected family member with SCD (Sudden Cardiac Death), or undiagnosed syncope when ventricular tachycardia or ventricular Fibrillation has not been excluded as the cause of syncope, who are receiving chronic optimal medical therapy, and who have reasonable expectation of survival with a good functional status for more than 1 y.
- Radiofrequency ablation can be useful as adjunctive therapy in management of patients with ARVC with recurrent ventricular tachycardia, despite optimal antiarrhythmic drug therapy.
ECG in ARVD
On ARVD.org the latest ECG criteria for ARVD are updated. To enhance detection of ECG abnormalities specific settings to record an ARVD ECG can be used: ECG settings to enhance recording of Epsilon waves.
In patients suspected to have ARVD both a normal 12 lead ECG and a Signal Averaged ECG (SAECG) are useful.
- Arvd ecg1.png
a patient with ARVD
- Arvd ecg2.png
- Arvd ecg3.png
Revised Task Force Criteria ARVD / ARVC
| Revised Task Force Criteria | |
|---|---|
| I. Global or regional dysfunction and structural alterations∗ | |
| Major | Minor |
|
By 2D echo:
By MRI:
By RV angiography:
|
By 2D echo:
By MRI:
|
| II. Tissue characterization of wall | |
| Major | Minor |
|
|
| III. Repolarization abnormalities | |
| Major | Minor |
|
|
| IV. Depolarization/conduction abnormalities | |
| Major | Minor |
|
|
| V. Arrhythmias | |
| Major | Minor |
|
|
| VI. Family history | |
| Major | Minor |
|
|
| |
References
Error fetching PMID 10768917:
Error fetching PMID 16949478:
Error fetching PMID 19366719:
Error fetching PMID 20215590:
Error fetching PMID 20172912:
- Error fetching PMID 10768917:
- Error fetching PMID 19366719:
- Error fetching PMID 8142187:
- Error fetching PMID 20215590:
- Error fetching PMID 20172912:
- Error fetching PMID 16949478: